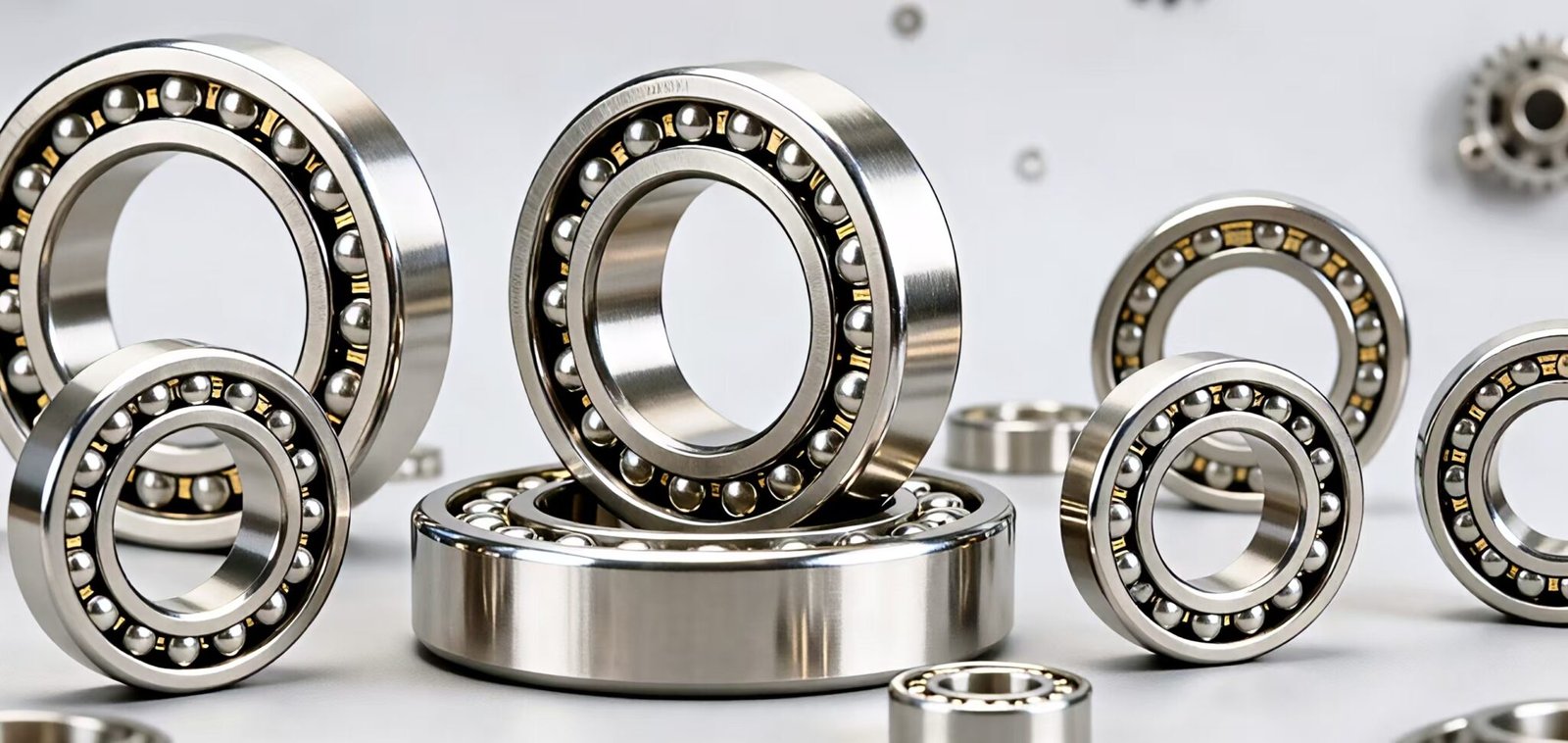

STAINLESS STEEL BEARINGS
The food and beverage (F&B) industry places extremely stringent requirements on bearings, primarily in two areas: hygiene and resistance to flushing corrosion. Stainless steel bearings are the ideal solution to these challenges.
In food processing plants, equipment must undergo daily high-temperature, high-pressure cleaning (such as CIP/COP cleaning procedures) and be treated with acidic or alkaline disinfectants/cleaners to eliminate bacterial contamination. Standard bearing steel is highly susceptible to rust and failure under such conditions. Stainless steel bearings (especially those made of SUS316) can withstand these harsh, humid, and chemically corrosive environments, ensuring continuous equipment operation.
Stainless steel bearings are typically used with food-grade grease (NSF H1 certified), which poses no harm even if it accidentally comes into contact with food. In filling machines, packaging machines, and sorting conveyors, the sealing design and corrosion resistance of stainless steel bearings effectively prevent rust and lubricant leakage, thus avoiding food contamination.
Request a Quote
Take the next step to forging your path to success. Request a quote from our team.
All Industries
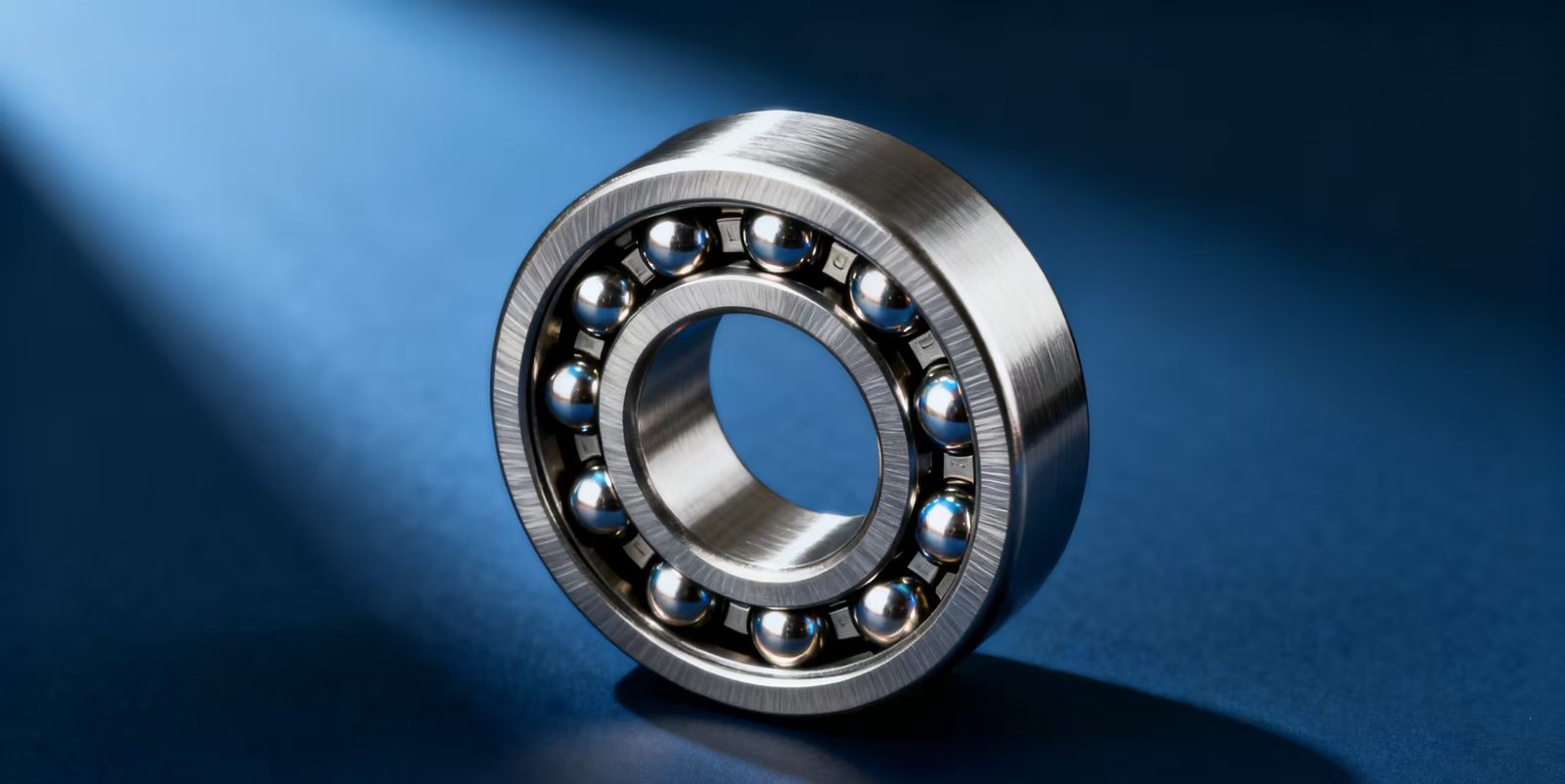

Characteristics and Advantages of Stainless Steel Bearings
he main advantage of stainless steel bearings lies in their **excellent corrosion resistance**. Compared to standard bearing steels (such as GCr15), stainless steel bearings effectively resist corrosion from moisture, water, steam, acid and alkali solutions, and chemicals, greatly extending their service life in harsh environments. Furthermore, due to their smooth surface and ease of cleaning, stainless steel also meets **high hygiene standards**, such as in applications in the food and medical industries. Some stainless steel materials also possess **weak magnetism or non-magnetism**, making them suitable for precision equipment sensitive to magnetic fields.
Common Materials and Structural Composition
The key components of stainless steel bearings (inner ring, outer ring, and rolling elements) are typically made of **martensitic stainless steel SUS440C**. This material, after heat treatment, achieves high hardness and wear resistance to ensure the basic load-bearing and operational performance of the bearing. Cages and seals, among other accessories, often utilize **austenitic stainless steel SUS304 or SUS316**, which offer superior corrosion resistance. SUS316, containing molybdenum, exhibits the best resistance to chloride corrosion and pitting, making it suitable for harsher chemical or marine environments.
These cost-saving advantages, combined with the extra durability, can mean better production rates and higher efficiency for your operations. When you succeed, we know we've succeeded.
304 Stainless Steel Bearings
It is the most common type of austenitic stainless steel bearing, with good corrosion resistance, heat resistance and machinability, and is widely used in food industry, medical equipment and other fields.

316 Stainless Steel Bearings
The addition of molybdenum to 304 stainless steel enhances its resistance to chloride ion corrosion, making it suitable for use in highly corrosive environments such as marine engineering and chemical equipment.

440 Stainless Steel Bearings
It belongs to martensitic stainless steel and is known for its high strength and high hardness. With proper heat treatment, the hardness can reach above 58HRC. It is suitable for applications with high requirements for precision and fatigue resistance, such as aviation, aerospace, and high-precision instruments.

420 Stainless Steel Bearings
Martensitic steel, commonly known as stainless iron, is magnetic, has good rust resistance, and high hardness. It is often used in industries with high requirements for precision and rust resistance, such as motorcycles and bicycles.
Main Application Areas
Due to their unique corrosion resistance and hygienic properties, stainless steel bearings are primarily used in special applications where standard bearings cannot meet the requirements. Typical applications include: **food processing and beverage bottling equipment** (requiring frequent rinsing and high cleanliness), **medical and pharmaceutical machinery** (requiring hygienic sterility), **chemical pumps and mixers** (contact with corrosive media), and **marine equipment and outdoor machinery** (resisting salt spray and humid environments). Although the ultimate load capacity and speed of stainless steel bearings are slightly lower than those of high-chromium steel bearings of the same size, their reliability and durability are irreplaceable in specialized applications.
Our Standard Forging Timeline
Scroll through to learn more about how our forging manufacturing process works:
Step 1/7
SolidWorks 3-D Modelling & Closed-Die Concept
LungChau Forge engineers turn your finished or semi-finished drawing into a validated 3-D SolidWorks model and multi-directional die layout within days.
Step 2/7
Die-Steel Machining on CNC Centres
We purchase premium die steel and machine the upper, lower and side rams to micron tolerances in our own machining centre.
Step 3/7
Certified Material Procurement
Alloys are ordered to the exact grade and size jointly signed off on the billet drawing, with full mill test certificates.
Step 4/7
Incoming Inspection & Precision Cutting
Bars are verified, then bandsaw or sheared into weight-controlled billets ready for heating.
Step 5/7
Green Heating – Induction or Natural-Gas Furnace
Billets are heated uniformly in an eco-friendly natural-gas or medium-frequency induction furnace to the optimal forging window.
Step 6/7
Multi-Ram Closed-Die Forging
Hot billets are shuttled within seconds to friction-screw or hydraulic presses where multi-directional rams form complex net-shape parts in one strike.
Step 7/7
UT / MT Non-Destructive Testing & Release
Every lot can be ultrasonically or magnetic-particle inspected to ASTM, EN or customer standards, ensuring defect-free delivery from LungChau Forge.
